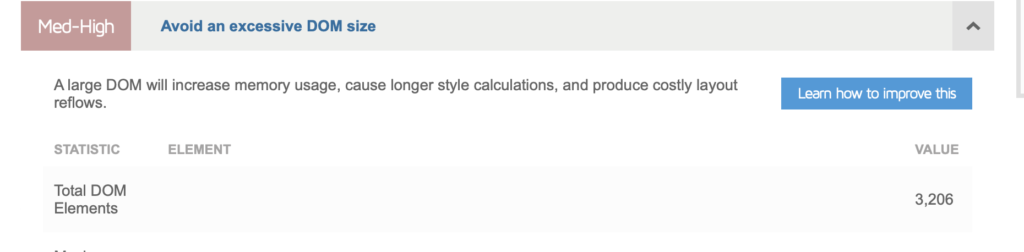
By analysing your website using Google PageSpeed Insights, You may have noticed an error such as «Avoid excessive DOM size»:

Or in GTmetrix «Reduce the number of DOM elements»:
What is the DOM?
When your browser receives an HTML document, it must be converted into a tree structure that is used for rendering and painting using CSS and JavaScript.
This tree structure is called DOM or Document Object Model.
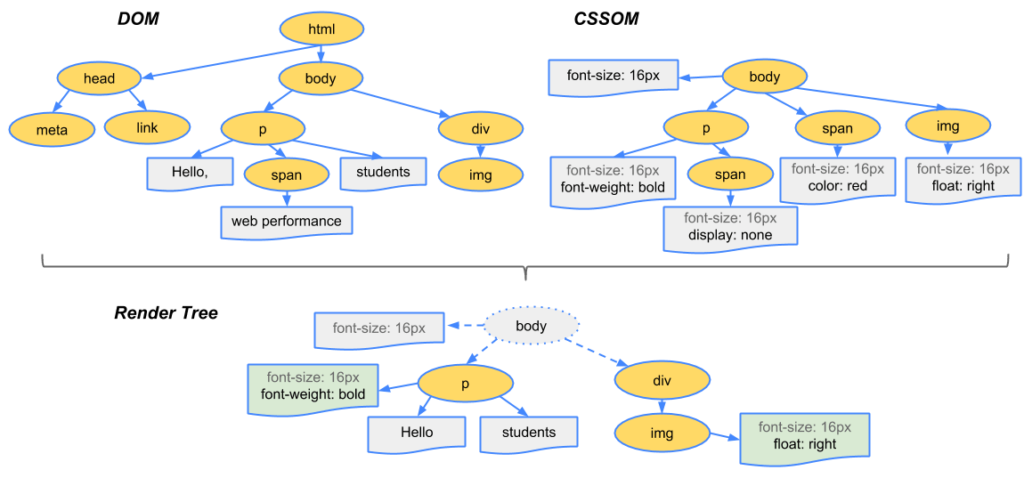
- Knots All HTML elements in the DOM are called nodes. (also known as «sheets» in the tree).
- Depth The length of the «branch» in a tree is called the depth. For example, in the diagram above, the «img» tag has a depth of 3 (HTML -> body -> div -> img).
- Child elements All child nodes of a node (without further branching) are child elements.
Lighthouse and Google PageSpeed Insights begin to flag pages if any of the following conditions are met:
- Presence of more than 1,500 nodes in total
- The depth is greater than 32 knots.
- Having a parent node with more than 60 child nodes
What impact does the size of the DOM have on performance?
Excessive DOM size can impact performance in various ways.
Longer analysis and rendering time (FCP) : A large DOM tree and complicated style rules (CSS) that require enormous processing power from the browser. The browser must analyse the HTML, build the rendering tree, etc. Every time the user interacts or something changes in the HTML, the browser must recalculate it.
Increased memory usage Your JavaScript code may have functions for accessing DOM elements. A larger DOM tree means that JavaScript uses more memory to process these elements. Here is an example of queries for manipulating DOMs with JS: document.querySelectorAll(‘img’), which lists all images and is commonly used by LazyLoad libraries.
Increases TTFB The larger your DOM, the larger the HTML document (in KB). Since more data needs to be transferred over the network, this increases the TTFB.
How can the size of the DOM be reduced technically?
For example, the technical reduction of the DOM size is done in this way:
Opt for:
instead of:
<div id="navigation-main">
<ul>
etc.
</ul>
</div>Essentially, you need to remove all possible HTML elements. You can also use Flexbox or Grid to further reduce the size of the DOM.
How to reduce the size of the DOM in WordPress?
Divide pages with multiple sections into several pages.
What if you have a page with several sections? Such as services, contact forms, products, blog articles, testimonials, etc.
Try dividing them into several pages and creating a link to them from the header, for example (navigation bar).
Apply lazy loading to elements on your site and paginate everything you can.
«Lazy load all possible elements. For example:
- Lazy load YouTube videos: Use WP YouTube Lyte or Lazy Load by WP Rocket.
- Limit the number of blog posts/products per page: Keep a maximum of 10 blog posts per page and paginate the rest.
- «Lazy load blog posts/products – Add a »Load more« button or infinite loading to load more blog posts or products.
- Lazy load comments: Using Disqus Conditional Load, for example. If you use native comments, use plugins such as Lazy Load for Comments.
- Pagination of comments: If you have hundreds of comments, this can also affect the size of the DOM. Paginate comments by going to Settings -> Discussion -> Split comments into pages.
- Limit the number of linked messages – Try to limit the number of linked messages to 3 or 4.
NB: Lazy loading images will not reduce the size of the DOM.
Do not hide unwanted elements using CSS.
Sometimes, it may be necessary to remove elements injected by the theme/builder. For example, adding to the shopping basket button on product pages, the rating button, author information, publication date, etc.
A quick solution is to hide them using CSS:
.cart-button {
display: none; ;
}
Although this solution seems easy to implement, it is not the optimal solution because you are distributing unwanted code to users (which includes both HTML markup and CSS styles).
Check your theme/plugin settings to see if there is an option to remove it. If not, find the corresponding PHP code and delete it.
Use well-coded themes and page builders
A good theme plays a major role in DOM size. Use well-coded themes such as GeneratePress or Astra.
Page builders also inject too many divs. Use builders such as Oxygen which do not inject unwanted divs and have more control over the HTML structure.
If you are not familiar with Oxygen, watch « Building a Website in Oxygen from Scratch.«
Conclusion
Other plugins or theme settings may be injecting too many divs. Example: «mega menu» plugins such as UberMenu.
They are sometimes crucial to the user experience of your website. However, there are also times when they are never used by users.
Perhaps your footer links are never clicked because most visitors only scroll down to 75% of the page.
Use tools such as HotJar or Google Analytics events to see what visitors are using and not using. Analyse, measure and iterate.
If you require assistance in optimising your website's performance or improving the loading speed of your strategic pages, WS Digital Consultancy, provides you with qualified and certified experts who are ready to assist you and offer solutions tailored to your website and in line with your budget. Contact us and request a personalised, FREE quote: Contact us

